What is Medicare?
Medicare is a national health insurance program, administered by the Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services of the U.S. federal government which started in 1966 under the Social Security Administration. It is a federal health insurance program for people who are 65 or older but can also cover those under 65 with a particular disability.
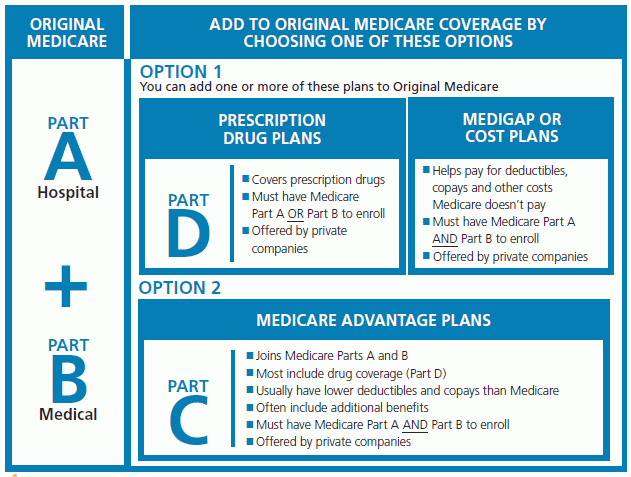
Generally, there are four main parts to Medicare.
Part A which primarily covers:
-
Hospital inpatient care
-
Skilled nursing facility
-
Limited, medically necessary, home health care
-
Hospice care
-
Part B which primarily covers:
-
Most medically necessary doctor services
-
Preventive services such as annual wellness exams and flu shots
-
Hospital and clinic outpatient services
-
Radiology (x-rays, CT scans and MRIs)
-
Laboratory tests
-
Outpatient mental health care
-
Durable medical equipment
-
Ambulance transportation
-
Limited, usually temporary, home health care
Part C which primarily covers:
-
Commonly known as Medicare Advantage - or- Option 2 (See below diagram)
-
Provides an alternative way to receive your Original Medicare (Part A and Part B) coverage
-
Typically, these plans are offered by private insurance companies that have contracts with the Medicare program
-
They cover everything Original Medicare covers (excluding hospice care, which remains covered through Medicare Part A)
Part D which primarily covers:
-
Commonly known as Medicare Supplement* -or- Option 1 (See below diagram)
-
Covers prescription drugs through private insurance companies contracted with the Medicare program
-
Such prescription drug cover stand-alone Medicare Part D Prescription Drug Plans, hence the Medicare formulary drug plans (Speak with a Medicare Insurance Agent or visit www.Medicare.gov for more information).
*Medicare Supplement (Medigap) plan helps pay for Medicare Part A and Part B out-of-pocket costs.